What’s The Difference Between A Single And A Double-Pole Breaker?
Company News, News 2025-12-25
Introduction: Navigating Your Circuit Breaker Panel
When you open your home’s electrical service panel, you’ll see an array of switches of different sizes. These are circuit breakers, your electrical system’s first line of defense against overloads and short circuits. Primarily, you’ll encounter two types: the narrower single-pole breaker and the wider double-pole breaker. While they may look similar, they serve distinct purposes and are fundamental to safe and efficient power distribution in both residential and commercial settings. This guide will clearly explain the differences in their function, wiring, and application to help you understand this essential component of your electrical infrastructure.
Single-Pole Circuit Breakers Explained
Single-pole breakers are the most common type found in panels, designed to protect individual 120-volt branch circuits.
Key Characteristics:
- Voltage & Amperage: They provide standard 120 volts and are typically rated for 15 to 20 amps.
- Physical Design: These breakers are narrow, occupying a single “slot” or pole on the panel’s bus bar.
- Internal Wiring: Internally, they monitor the current flow through one hot (live) wire. The circuit is completed by a return path through a separate neutral wire.
- Tripping Mechanism: In the event of an overload or short circuit on its specific circuit, only that single-pole breaker will trip and cut off power, leaving other circuits unaffected.
Typical Applications:
Single-pole breakers are dedicated to general-purpose, lower-power circuits throughout a building:
- General lighting fixtures and room outlets (receptacles)
- Small appliances (televisions, computers, chargers)
- Power tools, vacuums, and fans
- Outdoor lighting and garage door openers
Double-Pole Circuit Breakers Explained
Double-pole breakers are essentially two interconnected single-pole breakers with a common trip mechanism. They are designed to handle higher-voltage, higher-amperage circuits.
Key Characteristics:
- Voltage & Amperage: They deliver 240 volts (or 208V in some systems) and are commonly rated from 20 to 60 amps or higher for large equipment.
- Physical Design: They are twice the width of a single-pole breaker, occupying two adjacent slots on the panel and connecting to both “legs” of the incoming power.
- Internal Wiring: These breakers control two hot wires. A single neutral wire may be shared, or a separate neutral may be used depending on the appliance. The key feature is the tied handle, which ensures both hot legs are disconnected simultaneously.
- Tripping Mechanism: If a fault occurs on either of the two hot wires it controls, the entire double-pole breaker trips, cutting power to both legs. This is a critical safety feature for 240-volt appliances.
Typical Applications:
Double-pole breakers are reserved for large appliances and dedicated high-power circuits:
- Major home appliances: Electric ranges/ovens, clothes dryers, electric water heaters
- Central air conditioners and heat pumps
- Sub-panels (garage or workshop panels)
- Large shop tools like welders or industrial air compressors
*Note: A double-pole breaker can also be configured to protect two independent 120-volt circuits (often called a “tandem” or “cheater” breaker in specific panels), but this is subject to panel manufacturer guidelines and electrical codes.*
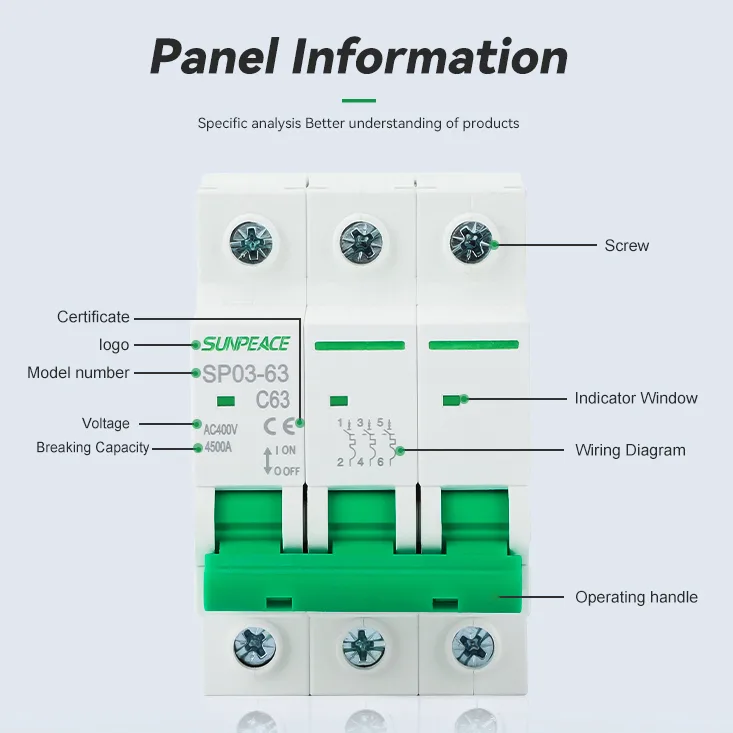
Core Differences at a Glance
| Feature | Single-Pole Breaker | Double-Pole Breaker |
|---|---|---|
| Width & Slots | Occupies 1 slot on the panel. | Occupies 2 adjacent slots. |
| Voltage Provided | 120 Volts | 240 Volts (or 208V) |
| Amperage Range | Typically 15-20 Amps | Typically 20-60+ Amps |
| Hot Wires Controlled | One hot wire. | Two hot wires (mechanically linked). |
| Primary Use | Standard lighting and outlet circuits for small appliances. | Large appliances and equipment requiring higher voltage/power. |
| Tripping Action | Only the affected single circuit trips. | A fault on either leg causes both legs to trip together. |
How to Choose and Important Safety Notes
Choosing the correct breaker is non-negotiable for safety and functionality.
- Match the Appliance Requirement: Always check the nameplate on your appliance for its required voltage (120V or 240V) and amperage. A 240V appliance must be connected to a double-pole breaker.
- Follow Wire Size and Code: The breaker’s amperage rating must correspond to the wire gauge (size) used in the circuit, as defined by the National Electrical Code (NEC). An oversized breaker can allow wires to overheat, creating a fire hazard.
- Consult a Professional for Installation: Working inside an electrical panel involves high risk. Installing, replacing, or troubleshooting breakers should be performed by a licensed electrician who can ensure compliance with all local codes and safety standards.
- Never Force or Modify a Breaker: Breakers are designed for specific panel models. Do not attempt to install a breaker that doesn’t fit perfectly, and never bypass a breaker that repeatedly trips—this indicates an underlying problem that needs diagnosis.
Reliable Circuit Protection with Sunpeace Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs)
Whether your project requires standard single-pole protection or dedicated double-pole breakers for major appliances, selecting reliable components is paramount. Sunpeace offers a comprehensive range of high-quality Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) designed for safety, durability, and performance.
Why Choose Sunpeace MCBs for Your Electrical Panel?
- Full Product Range: Sunpeace manufactures both single-pole and double-pole MCBs in various amperage ratings, ensuring you find the exact match for your residential, commercial, or light industrial application.
- Engineered for Safety: Our breakers are designed to meet or exceed international safety standards, providing precise thermal-magnetic protection against overloads and short circuits for reliable operation.
- Factory-Direct Value: As a direct manufacturer, Sunpeace provides robust electrical components with a focus on quality control, offering excellent value without compromising on performance or safety.
- Technical Application Support: Our expertise extends beyond products. We can provide guidance on product selection and application to support your specific project requirements, from simple replacements to new installations.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between single-pole and double-pole breakers is key to comprehending your home’s electrical system. Single-pole breakers safely manage your everyday 120-volt needs, while double-pole breakers are essential for powering your large 240-volt appliances. Always prioritize correct sizing and professional installation to maintain a safe electrical environment.
For your circuit protection needs, from panel upgrades to equipment installations, consider the reliability of Sunpeace MCBs. Investing in properly specified, quality components is an investment in the long-term safety and functionality of your electrical system.
Contact US
Facebook:Sunpeace electric
YouTube:Sunpeace electric


